A Promising New Photosensitizer for the Photodynamic Therapy of Hypoxic Tumors
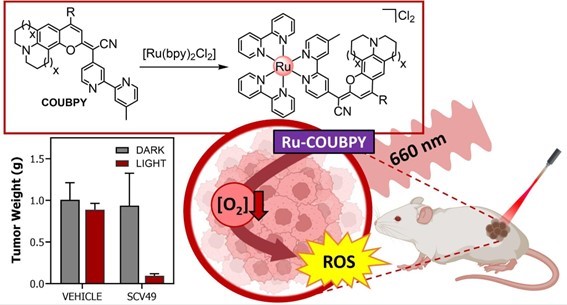
In a recent article published in the Journal of American Chemical Society, the group of Prof. Gilles Gasser at the Institute of Chemistry for Life and Health Sciences at Chimie ParisTech-PSL, in collaboration with the group of Vicente Marchan at the University of Barcelona, reported a novel family of potent photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy (PDT) that exhibit impressive nanomolar potency under photo-activation within the therapeutic window, and this in both normoxic and hypoxic conditions.
This is of high interest since hypoxia is a hallmark of many solid tumors and is linked to increased cancer aggressiveness, metastasis, and resistance to conventional therapies, leading to poor patient outcomes. The researchers could demonstrate that their lead compounds, SCV49, had a favorable in vivo pharmacokinetics profile, excellent toxicological tolerability, and potent tumor growth inhibition in mice bearing subcutaneous CT-26 tumors at doses as low as 3 mg/kg upon irradiation with deep-red light (660 nm). Overall, the results of this study demonstrate that SCV49 is a strong candidate for further preclinical development, particularly for treating large hypoxic solid tumors.
